Call: (905) 689-8282
Sports Therapy Blog
Our blog is your definitive online resource for valuable information regarding chiropractic and physiotherapy treatments, helping you to better understand these beneficial therapies. Through a variety of engaging and educational posts, we seek to provide insightful tips, latest research findings, and practical advice on how to maximize the benefits of our chiropractic and physiotherapy services.
By Kevin Brownell
•
February 4, 2025
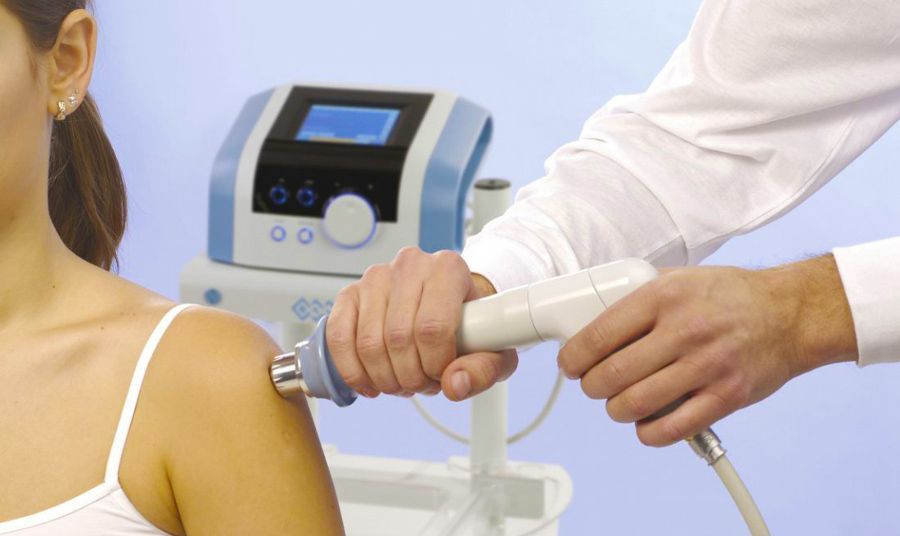
In modern medicine and rehabilitative care, the quest for innovative treatments is constant, driven by a desire to offer better health outcomes and enhance patient experiences. One such innovation that's making waves—quite literally—is shockwave therapy. This unconventional approach to healing has gained significant traction in recent years, particularly within the sports and physical therapy realms, owing to a remarkable range of benefits. At Alta Spine and Sports Therapy , a leading clinic in Waterdown offering cutting-edge treatments, we're proud to introduce shockwave therapy as part of our comprehensive suite of services. Our team has witnessed firsthand the impressive results this therapy can produce, from accelerated healing to significantly reducing chronic pain levels. Whether you're an athlete looking to get back on the field, or a patient seeking to regain mobility, the power of these shockwaves should not be overlooked. Understanding Shockwave Therapy Before we explore the extensive benefits, it's essential to understand what shockwave therapy entails. Despite its name, the 'shockwaves' used in this treatment are not electrical but are high-energy sound waves—acoustic pulses with a kinetic energy that can be targeted to specific anatomical areas. These sound waves are generated outside the body by a device that transmits mechanical forces to the tissues. The resultant effects inside the body prompt a series of regenerative responses, including increased blood flow, the formation of new blood vessels, and the stimulation of healing factors within tissue. Essentially, this non-invasive therapy jumpstarts the body's natural healing mechanisms to promote faster recovery. The Versatility of Shockwave Therapy The applications for shockwave therapy are both varied and potent, extending to an impressive array of musculoskeletal conditions. The most remarkable aspect of shockwave therapy is its ability to treat these ailments without invasive procedures or prolonged recovery times. Benefits for Athletes Athletes, no strangers to the wear-and-tear of intense physical activity, stand to gain much from shockwave therapy. High-impact sports can lead to an array of injuries, such as tendonitis, bursitis, and muscle strains. These injuries often result in significant downtime, reducing an athlete's training hours and, subsequently, their performance. Shockwave therapy offers a faster, more effective healing process, enabling athletes to return to their activities with renewed vigor. Chronic Pain Management For individuals struggling with chronic pain, shockwave therapy presents a glimmer of hope in long-term management. It's been particularly effective for those with conditions like plantar fasciitis, a common cause of heel pain, and Achilles tendinopathy, a chronic tendon disorder that affects the back of the lower leg. By targeting these areas with shockwave energy, patients can experience a notable reduction in pain symptoms, often with lasting effects. Enhancing Rehabilitation Post-surgery rehabilitation is a critical phase in the healing process, and shockwave therapy has been found to enhance this stage significantly. It can aid in breaking down scar tissue, improve joint mobility, and alleviate post-operative pain. The non-invasive nature of shockwave therapy also makes it a desirable option for those wary of invasive procedures or for whom surgery is contraindicated. Evidence-Backed Results We don't make these claims lightly. There is a growing body of clinical evidence supporting the positive outcomes of shockwave therapy across various patient populations. From random controlled trials to systematic reviews, the consensus is that this therapy can yield tangible benefits in terms of pain reduction, functional improvement, and speedier recovery. Accelerated Tissue Repair Studies have revealed that shockwave therapy accelerates the body's natural tissue repair processes, including the regeneration of blood vessels and connective tissue. This evidence is foundational to understanding how shockwaves can produce enduring results, helping patients regain their quality of life more rapidly than traditional treatments alone. Long-Term Healing The long-term benefits of shockwave therapy are particularly heartening. Patients who undergo this treatment are less likely to experience a recurrence of their symptoms, suggesting that the regenerative effects are not just temporary but contribute to lasting healing. Improving Quality of Life The reduction in chronic pain and functional improvement that come with successful shockwave therapy can have profound effects on a patient's quality of life. It can restore the joy in movement for those who've been hindered by pain and offer a renewed sense of hope for a life unhindered by musculoskeletal limitations. Getting Started with Shockwave Therapy If you're intrigued by the idea of shockwave therapy and its potential to enhance your well-being, the next step is to seek consultation with our knowledgeable healthcare professionals at Alta Spine and Sports Therapy. With a patient-centered approach and a commitment to excellence, we can assess your condition and determine whether shockwave therapy is appropriate for your treatment plan. Remember, the benefits of this therapy extend beyond the physical to the practical, emotional, and psychological aspects of health. It's about reclaiming life, joy, and the pursuit of what makes us feel alive, pain-free, and whole. In the healing arc of medicine, shockwave therapy represents a profound moment. It's a technology that not only heals but empowers patients to take charge of their recovery. It's a new wave in healing—one that all who value vitality and mobility should ride. Don't settle for living with pain. Discover the transformative benefits of shockwave therapy for yourself at Alta Spine and Sports Therapy. Take that first step towards a better, more vibrant you. Your body, your life, and your future will thank you.

By Kevin Brownell
•
January 8, 2025
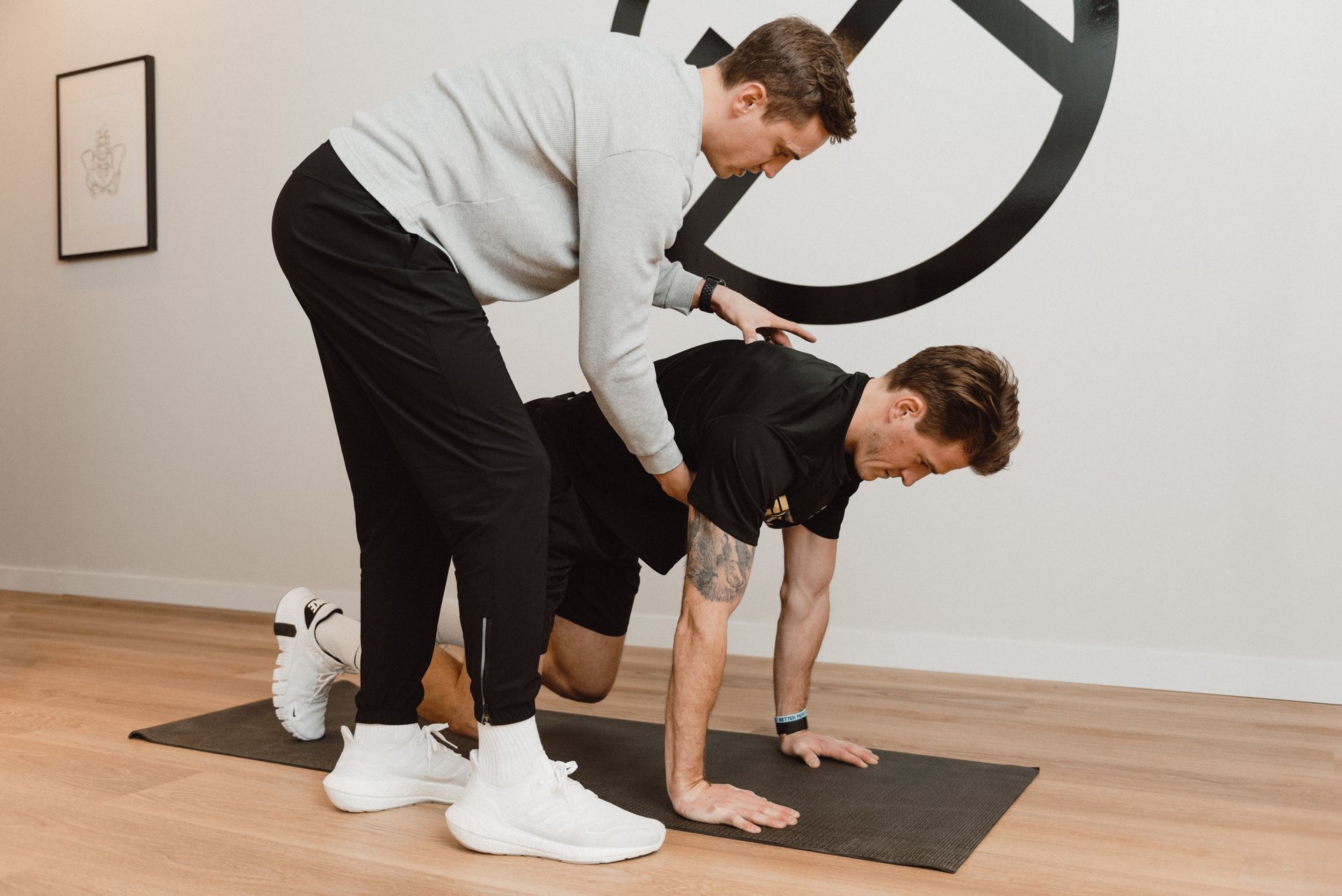
Engaging in sports and physical activity is a fantastic way to stay healthy, challenge your body, and even find community. However, the very nature of athletics—especially when it involves elements of intensity, speed, or agility—can sometimes lead to injuries. Whether you're a seasoned athlete or a weekend warrior, understanding the common types of sports injuries is essential for both preventing and addressing them. In this comprehensive post, we'll take a deep dive into some of the most frequent injuries that can occur, illuminating the differences between acute and overuse injuries, and explaining why professional guidance is vital to your recovery and future performance. Understanding the Difference Between Acute and Overuse Injuries Before we explore specific types of injuries, it's crucial to establish the two broader categories they fall into—acute and overuse. Acute Injuries are sudden and typically caused by a specific event, such as a collision, fall, or rapid movement that overloads the body's tissues. Examples of such injuries include a sprained ankle from a poorly landed jump or a dislocated shoulder from a fall during contact sports. Overuse Injuries , on the other hand, develop gradually over time, typically from repetitive trauma to the muscles, tendons, or joints without allowing them sufficient time to heal. Runners, for instance, are familiar with conditions like runner's knee or Achilles tendinitis, which can plague them after months or years of high-impact activity. Both types of injuries require attention, but overuse injuries can often be more insidious, as their slow progression may go unnoticed until significant symptoms appear. The Anatomical Insight of Sprains and Strains Sprains and strains are two of the most common sports injuries, occurring almost as frequently as the sports themselves. Understanding the anatomy involved and the specific characteristics of each injury is the first step to navigating your treatment and recovery. A Closer Look at Sprains Sprains involve ligaments, the tough bands of fibrous tissue that connect bones within a joint. When a ligament is stretched beyond its limits, it can tear, leading to what is commonly known as a "twisted" joint. Sprains are graded according to their severity: Grade I is a mild stretch or tear of the ligament with minor swelling and tenderness. Grade II is a significant but incomplete tear of the ligament, often leading to moderate swelling, bruising, and joint instability. Grade III is a complete tear or rupture of the ligament, resulting in severe pain, swelling, and an inability to bear weight on the joint. Understanding Strains Strains are injuries to muscles or tendons, which are the cords of tissue that connect muscle to bone. Like sprains, strains can vary in severity: Grade I strains involve overstretched muscles or tendons, leading to mild discomfort and minimal impact on athletic performance. Grade II strains are more severe, resulting in partial tears, significant pain, swelling, and difficulty moving the affected muscle. Grade III strains are complete tears or ruptures, causing intense pain, severe swelling, and a total inability to use the affected muscle. Knowing the difference in the type of tissue affected and the grading of the injury can help you understand the recommended course of treatment and rehabilitation. The Role of Proper Assessment and Diagnosis in Injury Management One of the most common mistakes athletes make is minimizing the importance of a professional assessment and diagnosis in the heat of the moment or when dealing with what seems like a minor ache or pain. However, a proper diagnosis not only provides peace of mind but also ensures that you receive the appropriate treatment, which can significantly affect your recovery time. A healthcare professional, often specializing in sports medicine or orthopedics, can use a combination of physical examination, medical history inquiry, and, if necessary, imaging studies like X-rays or MRI scans to diagnose your injury accurately. From there, they guide you in developing a comprehensive treatment plan that may include rest, immobilization, physical therapy, or even surgery, depending on the severity of the injury. An accurate diagnosis is especially critical for overuse injuries, as they may require changes to your training routine, equipment, or even the way you perform certain activities. Ignoring or mistreating an overuse injury can lead to chronic pain and long-term limitations in mobility and participation. Natural Recovery Versus Professional Intervention While our bodies are remarkably adept at healing, relying exclusively on natural recovery may not be the most effective or efficient approach—especially if you're eager to return to the sport or activity you love as quickly as possible. Professional intervention, whether it's through manual therapy, rehabilitation, or education, can play a significant role in your recovery process. The Benefits of Manual Therapy Manual therapy encompasses a variety of techniques, such as massage, mobilizations, or manipulations, designed to relieve pain, improve flexibility, and enhance tissue healing. For acute injuries, early intervention with manual therapy can restrict swelling, aid in the repair of damaged tissue, and prevent the formation of scar tissue. Similarly, for overuse injuries, regular sessions with a skilled therapist can identify and address muscular and joint imbalances that contribute to the injury, and provide advice on proper movement to avoid re-injury. Proper Rehabilitation Rehabilitation is a structured program that involves exercises, stretches, and potentially the use of specialized equipment to regain strength and function in the injured area. The goal is to return the athlete to their pre-injury level of activity, with reduced risk of re-injury. Rehabilitation can be broken down into four main phases: Phase 1 (Immediate/Restorative) focuses on reducing pain and swelling, restoring range of motion, and preventing muscle atrophy. Phase 2 (Recovery) aims to restore strength, endurance, and full range of motion. Phase 3 (Functional) centers on re-establishing balance, coordination, and proprioception, which is the body's ability to sense its location and movement in space. Phase 4 (Return to Activity) ensures that an athlete is fully physically prepared to return to their prior level of activity without pain or restriction so that they don't fall back into bad habits. The Value of Education Receiving guidance on injury management, understanding the healing process, and learning appropriate strategies to prevent future injuries is invaluable. Education may involve discussions about proper warm-up and cool-down routines, the use of protective gear, cross-training, modifying workouts during recovery, or adopting a healthier lifestyle to support your athleticism. Reintegrating Into Your Sport After an Injury Reintegrating into your sport after an injury can often be as challenging—mentally, at least—as the injury itself. Athletes may feel apprehensive, physically unprepared, or concerned about re-injury once they step back onto the field, court, or track. A gradual, structured approach to returning to play is essential. The Importance of a Phased Return A phased return involves a systematic reintegration into sports activities over time. This may include progressing from light drills to full practices, from controlled play to competitive play, and, eventually, from limited game time to a return to your standard level of participation. Each phase provides an opportunity to assess your comfort, physical response, and readiness to move forward. It's important to listen to your body during this transition and communicate openly with your healthcare team, coaches, and trainers about your progress and any concerns you have. Mental Preparation and Support Injuries can be a significant blow to an athlete's confidence. Mental preparation and support, such as sports psychology, can help address any performance anxiety or lingering negative emotional impact. Techniques like visualization, goal-setting, and positive self-talk can aid in the mental recovery process and prepare you for competition once more. Recovering from a sports injury is not just a physical challenge—it's also a mental and emotional one. Professional mental skills training can help you regain your competitive edge and confidence. The Role of Good Nutrition and Hydration in Recovery Nutrition and hydration play an integral role in the recovery process from sports injuries. Injuries increase the body's requirement for nutrients that support tissue repair, recovery, and immune function. What to Eat Eating a well-balanced diet rich in lean protein, whole grains, healthy fats, and a variety of fruits and vegetables can help meet the increased nutritional needs associated with healing. Specific nutrients that may aid recovery include: Protein , for the building and repair of injured tissues. Anti-inflammatory foods , such as fatty fish, nuts, and leafy greens, to reduce swelling and support the body's natural healing processes. Vitamin C and Zinc , which are known to support the immune system. Proper Hydration Water is essential for the body's metabolic processes, including those involved in repair and recovery. Dehydration can slow down the healing process and reduce the effectiveness of physical therapy and rehabilitation exercises. Ensuring that you are drinking enough water is crucial, but you may also need to increase your intake of electrolytes if you're recovering from an injury that involves significant perspiration, such as those that occur in high-intensity sports. Conclusion and Next Steps Understanding the spectrum of sports injuries—how they occur, how they're assessed, and how they're treated—is a crucial aspect of every athlete's knowledge base. By arming yourself with information on injury prevention and recovery, you not only safeguard your immediate future in your chosen sport but also set the stage for a lifelong commitment to holistic well-being. Remember, the road to recovery is not a straight line, and setbacks are natural. However, with a thoughtful approach that combines self-awareness, professional guidance, and a comprehensive treatment plan, you can come back from an injury even stronger and more informed than before. If you have experienced a sports injury, consulting with a healthcare professional at Alta Spine and Sports Therapy can ensure that you receive the care and treatment necessary to get back to doing what you love. Our team of experts in chiropractic, physiotherapy, and massage therapy can guide you through a personalized rehabilitation program tailored to your specific needs and goals. Don't stay sidelined—take the first step toward recovery and book your appointment today.

By Kevin Brownell
•
December 5, 2024
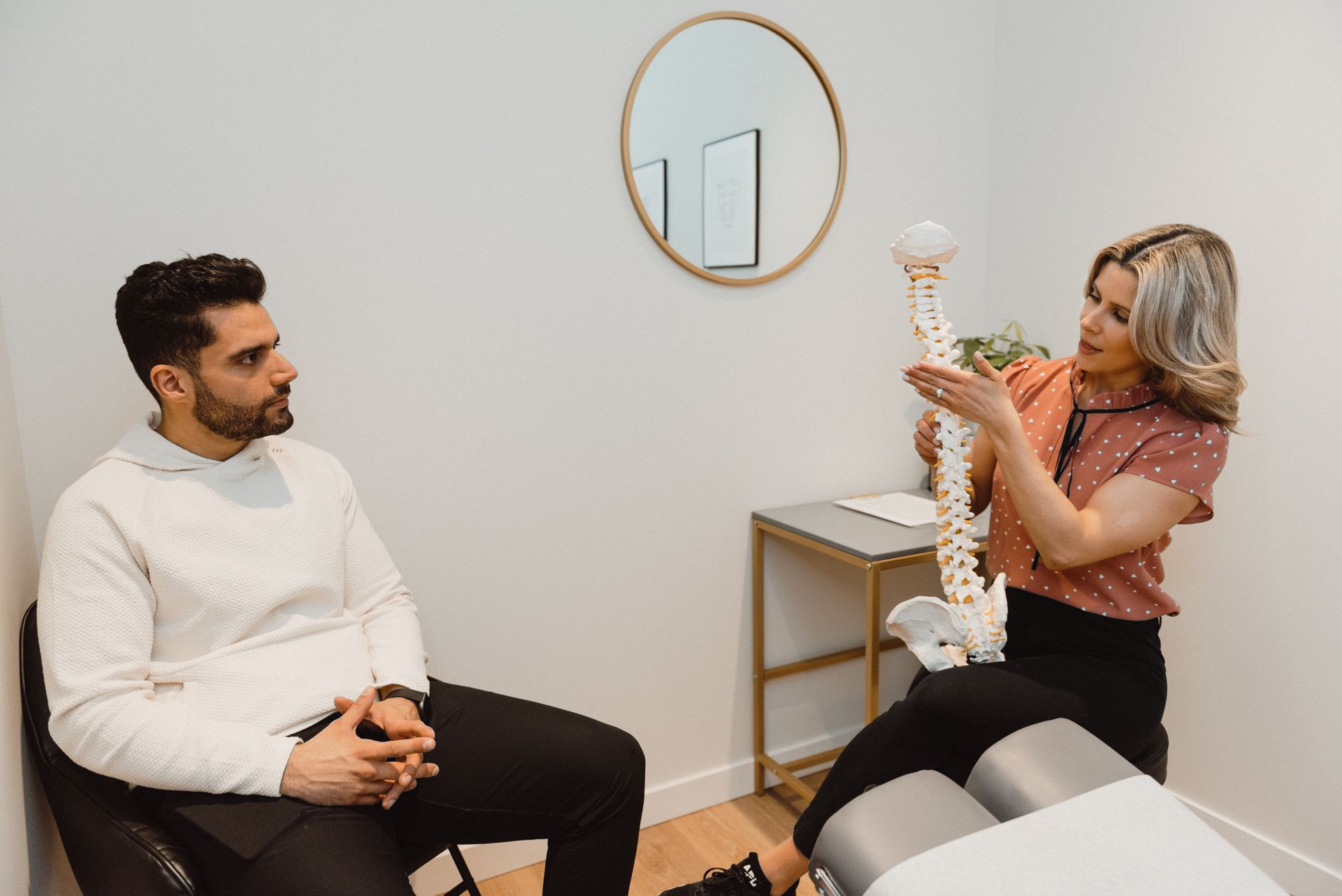
Long days, warm evenings, and a swelling urge to break free from winter's sedentary clutches—summer heralds the season of movement. For fitness enthusiasts, it's a summons to lace up running shoes, pump up bike tires, and hit the trails with renewed vigor. However, as the adage goes, enthusiasm can breed eagerness and sometimes, lack of caution, leading to overuse injuries that can banish the best intentions to the bench. In this article, we'll explore the art of listening to your body, understanding the nuances of overuse injuries, and how strategic caution can be the key to a healthful, sustained fitness routine. This is more than cutting edge sports science or elite athlete anecdotes; it's the pulse of your physical well-being that beats beneath the excitement of summer's opportunities. The Anatomy of Overuse Injuries Overuse injuries are the silent saboteurs of the body, often disguised in a dull ache or persistent discomfort. While the thrill of pushing your limits can be exhilarating, the fine line between progress and peril lies in the recognition of these early warning signs. But what exactly are overuse injuries? They're the result of repetitively stressing the same muscles, joints, or tissues without allowing for adequate recovery. Common examples include tendinitis, stress fractures, and muscle strains. Unlike acute injuries from sudden impact or falls, overuse injuries develop over time—a slow crescendo of warning signals only truly apparent in hindsight. Prevention through Proprioception How then to remain injury-free while pursuing your fitness dreams? The answer is as simple as it is complex—proprioception. This innate sense of the relative position of neighboring parts of the body and the effort of movement ensures you don't slam down too hard with each step, pivot sharply without a pivot point, or cycle with unyielding vigor on every hill. Incorporating exercises that challenge balance, such as single-leg squats, lunges, and balance boards, can enhance proprioception. These exercises, in turn, foster a heightened awareness of body positioning and, crucially, a decreased likelihood of landing in the crosshairs of an overuse injury. Gradual Progression: The Tortoise Wins the Race Whether you're adjusting to a new activity or ramping up your current routine, the sage advice of the tortoise holds true—slow and steady wins the race. Gradual progression allows your body to adapt to new demands, minimizing the risk of overuse. If you're a runner, this might mean following the 10% rule—increasing your weekly mileage by no more than 10% compared to the previous week. For weightlifters, it could entail starting with lighter weights and working your way up over successive sessions. The principle is universal; it's about giving your body time to adjust and become resilient to the increased load. Rest and Recovery: The Unsung Heroes of Fitness In a culture that celebrates hustle and highlights, rest and recovery might seem like anathema to progress. Yet, they are the unsung heroes that allow your body to heal and grow stronger. Strategic rest days should be woven into your training plan, as should lighter recovery exercises that shift your focus from intensity to quality of movement. Yoga, swimming, and brisk walks are excellent choices, as they improve flexibility, maintain cardiovascular health, and provide a mental breather from the grind. The Mental Component: Pushing Through vs. Listening The determination to push through can be both the athlete's strongest ally and most subtle foe. It's essential, of course, for surpassing plateaus and reaching new benchmarks. Yet, it also demands the humility to recognize when your body is asking for a reprieve. Developing the skill to discern between physical discomfort and true pain is key. Discomfort might signal a challenging workout, but pain, particularly sharp or localized, is a call to action—reassess, adjust, and potentially seek professional advice. Vanity metrics, such as mile times or personal records, should never eclipse the primary goal of fitness—health and well-being. Realigning Your Routine for Success With the surge of outdoor activities beckoning, summer entices us to reach for the skies. However, it's the grounded approach that ensures longevity and enjoyment in your fitness pursuits. Realign your aspirations with achievable goals that prioritize your body's signals over abstract milestones. Update your training plans with a focus on incremental improvements rather than rapid advancements. And most importantly, respect the process of recovery as much as you do the rigors of exercise. Ensuring an injury-free season of activity is more than an exercise in smart programming—it's a lifestyle that champions the long game of health and sustainability. This is the story of fitness not merely in its endpoint, but in the ebb and flow of the everyday. It is a tale that fortifies the resolve to listen, learn, and ultimately, love the body that carries you through the rhythms of a well-lived summer.

By Kevin Brownell
•
November 5, 2024
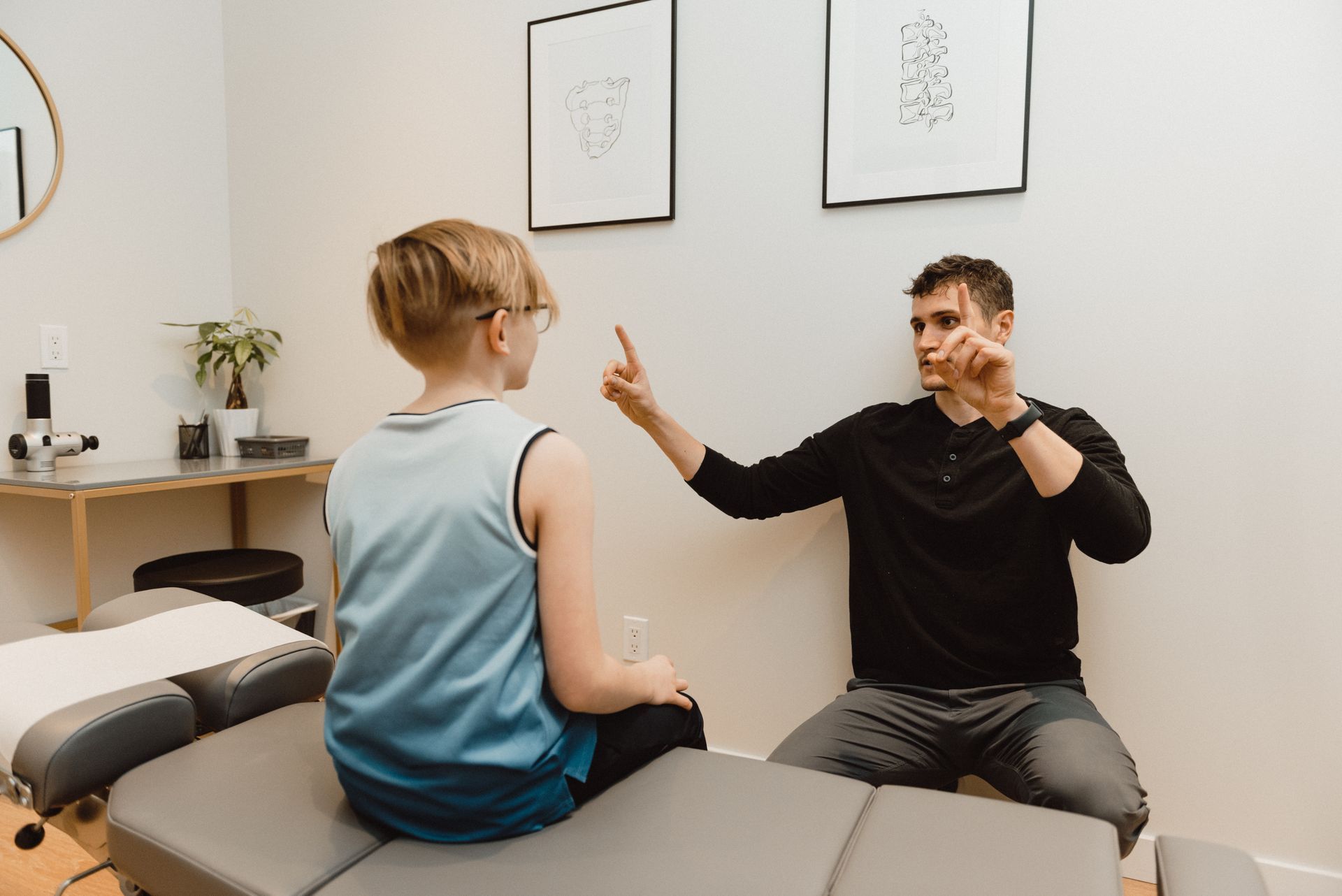
For youth athletes, the playing field is a stage for triumph, teamwork, and growth. Yet, with the rising competitiveness in youth sports, the risk of experiencing a concussion has become a critical concern for parents, coaches, and players alike. In this blog post, we'll explore the importance of proper concussion assessment and treatment , and how these protocols not only secure immediate safety but also pave the way for better long-term health outcomes for our young athletes. Understanding Concussion Assessment A concussion i s not just a bump on the head; it's a type of traumatic brain injury that demands immediate attention. The first step in safeguarding our youth is thorough and proper assessment. When a potential concussion occurs, the value of an accurate diagnosis cannot be overstated. It's the initial assessment that guides the entire treatment process; missteps here can have ramifications that extend far into an athlete's future. A key aspect of concussion care involves baseline concussion assessments conducted before the season even starts. These assessments serve as a critical tool, providing a pre-injury snapshot of an athlete's brain function, which can include memory, reaction time, speed, and concentration. When a suspected concussion occurs, healthcare providers can compare the athlete’s post-injury condition to their baseline assessments. This comparison is invaluable as it assists in accurately evaluating the impact of the injury and making informed decisions regarding the management of the athlete's recovery. Equally important, baseline assessments underscore the commitment of coaches, parents, and sports organizations to prioritize athlete safety from the outset of the sporting season. Recognizing the signs of a concussion goes beyond observing obvious symptoms like disorientation or loss of consciousness. Subtle cues such as headache, dizziness, confusion, or even changes in mood can all signal a concussion. It's vital for coaches and parents to be well-informed and vigilant observers, ready to take action and seek professional assessment if they suspect a concussion. The Road to Recovery Once a youth athlete has been diagnosed with a concussion, the process for recovery must be tailored to their specific needs. No two concussions are the same, and as such, treatment plans should be individualized. Rest is often prescribed initially, but the progression back to normal activity must be gradual and carefully monitored by healthcare professionals specializing in concussive injuries. Concussion recovery is multifaceted, reflecting the complex nature of the injury itself. Key components of a concussion include vestibular (related to balance and spatial orientation), metabolic (biochemical processes within the brain), visual (how the brain processes what the eye sees), and cervicogenic (originating from the neck) aspects. Each of these components can be affected differently and may manifest distinct symptoms. After the initial rest period, it's crucial to accurately identify any lingering symptoms that might be associated with these areas. This targeted approach allows healthcare professionals to develop a more effective, personalized treatment plan that addresses each specific symptom, thus facilitating a safer and more efficient return to daily activities and sports participation. One of the most important aspects of recovery is determining when a young athlete is ready to return to play. Returning too soon increases the risk of a second concussion, which can result in more severe brain injuries. Thankfully, modern protocols and assessments, including cognitive and physical tests, inform decisions that prioritize the athlete's health and future well-being. Safer Return to Play Proper care post-concussion leads to a safer return to the sport. There's a growing emphasis on ‘return to play’ protocols that emphasize the athlete's complete recovery. These guidelines offer a step-by-step approach to resuming activity so that the young athlete's brain is given ample time to heal properly. In doing so, we significantly reduce the risks of repeated injuries and the possibility of long-term health issues. Parents and coaches can breathe easier knowing that adherence to these protocols increases the safety of their youth athletes, not just for the current season but for their entire athletic futures. Prevention Over Cure While treatment post-concussion is critical, prevention remains paramount. Educational programs for coaches, parents, and youth athletes themselves can foster a culture of safety that helps minimize the risk of concussions. Teaching techniques that avoid dangerous play are basic yet effective strategies. Furthermore, promoting honest communication among teammates, where players feel supported in reporting symptoms, fundamentally changes the safety landscape of youth sports. Conclusion Concussions in youth sports are a serious matter. Through proper assessment, mindful treatment, and rigorous return to play protocols, we can protect the bright futures of young athletes. Parents and coaches have a pivotal role in this endeavor—a role that starts with education and ends with enforcement. By prioritizing safety today, we safeguard the health of the following generation while maintaining the integrity and enjoyment of youth sports.
Our Information
Address
Phone
Business Hours
- Monday
- -
- Tue, Thu
- -
- Wednesday
- -
- Friday
- -
- Sat - Sun
- Closed
Business Hours
- Monday
- -
- Tue, Thu
- -
- Wednesday
- -
- Friday
- -
- Sat - Sun
- Closed